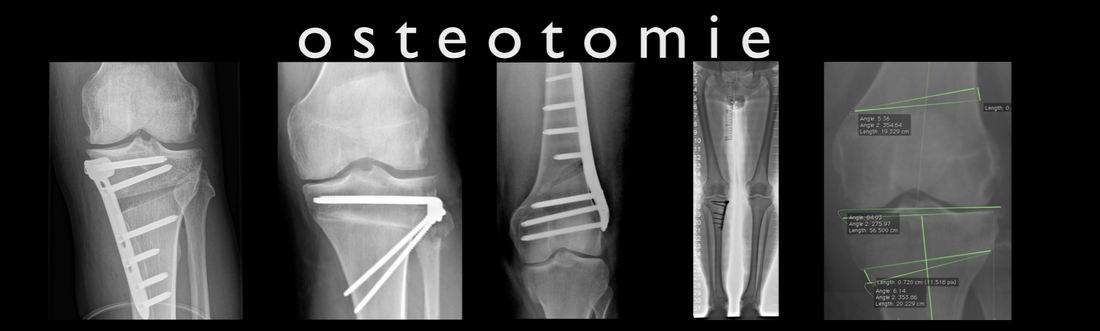
Osteotomy
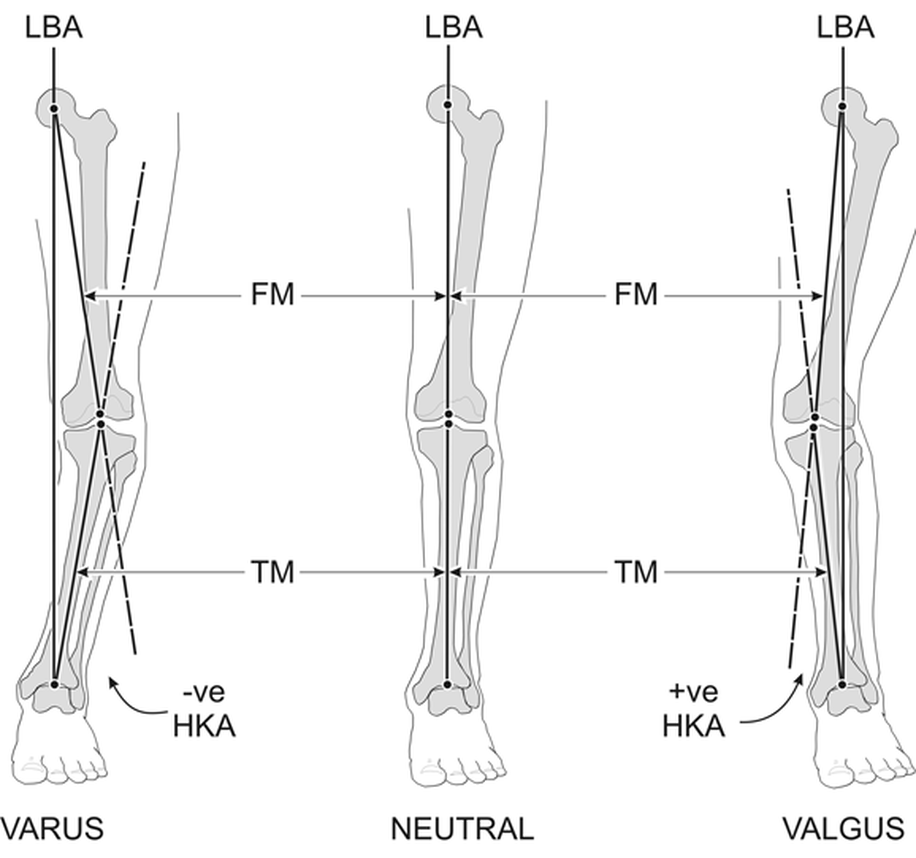
The normal knee has a straight axis, which means that the load on the leg passes through the middle of the knee. If the load axis of the leg deviates, one speaks of O-legs or X-legs; an axis correction or osteotomy of the knee is then the appropriate solution.
Causes The axis of the leg can deviate from the normal axis for a number of reasons: A congenital axis defect, Previous surgery (e.g. complete removal of the inner or outer meniscus) A previous accident with a fracture that healed in an abnormal position.
Types The axial deviation of the leg can be in 2 directions: We speak of a bow leg or varus knee when the load axis runs through the inner part of the knee. This leads to overload and faster cartilage wear of the inside of the knee. We speak of an X-leg or valgus knee if the load axis runs through the outer part of the knee. This leads to overload and faster cartilage wear of the outside of the knee. Operation The axis deviation can be corrected surgically by means of an open wedge or closed wedge osteotomy. In this way we can protect the overloaded part of the knee against premature wear and tear or osteoarthritis. This correction is only useful if the other parts or compartments of the knee are still in good condition. During an open wedge osteotomy, the bone is cut through with a saw and chisel and then progressively spread open until the desired correction is achieved. This correction is checked during the procedure by means of fluoroscopy. During a closed wedge osteotomy, a triangular wedge is removed and the leg is folded. Open wedge corrections are most commonly performed except in smokers and obese individuals where closed wedge corrections are performed.
Causes The axis of the leg can deviate from the normal axis for a number of reasons: A congenital axis defect, Previous surgery (e.g. complete removal of the inner or outer meniscus) A previous accident with a fracture that healed in an abnormal position.
Types The axial deviation of the leg can be in 2 directions: We speak of a bow leg or varus knee when the load axis runs through the inner part of the knee. This leads to overload and faster cartilage wear of the inside of the knee. We speak of an X-leg or valgus knee if the load axis runs through the outer part of the knee. This leads to overload and faster cartilage wear of the outside of the knee. Operation The axis deviation can be corrected surgically by means of an open wedge or closed wedge osteotomy. In this way we can protect the overloaded part of the knee against premature wear and tear or osteoarthritis. This correction is only useful if the other parts or compartments of the knee are still in good condition. During an open wedge osteotomy, the bone is cut through with a saw and chisel and then progressively spread open until the desired correction is achieved. This correction is checked during the procedure by means of fluoroscopy. During a closed wedge osteotomy, a triangular wedge is removed and the leg is folded. Open wedge corrections are most commonly performed except in smokers and obese individuals where closed wedge corrections are performed.
3D planning
3D planning makes it possible to study the axis deviation in detail and to carry out the correction very precisely. That is why we are increasingly using this technique for both simple and complex corrections (malunion). Our service has developed a dedicated 3D analysis and execution platform where we want to remain progressive in patient-specific applications around osteotomy.
Frequently Asked Questions
When can I drive? This depends on the strength and coordination of your knee. Your physiotherapist can assess when participation in traffic is responsible again. Usually this is possible from week 6-8
When can I resume work? This obviously depends on the type of work and can vary from 8 weeks to 6 months How long should I get the injections for DVT? 30 days When can I shower? As soon as the wound is dry, a waterproof bandage can be applied so that showering is possible!
How long will I stay in hospital? Classic 1 night.
Complications? Blood clotting and phlebitis may occur. If these clots break free, they can travel to the lungs and cause a life-threatening pulmonary embolism. To minimize this risk, injections with a blood thinner are therefore given for 30 days. Infections are rarely seen but can occur either around the wound or deeper around the plate. Superficial wound infections can in most cases be treated with antibiotics. Deep infections usually require additional surgery. Antibiotics are given during the procedure to minimize the risk of infection. Delayed healing of the osteotomy is more common in smokers and diabetics. Smoking cessation is therefore recommended for this type of procedure!
When can I resume work? This obviously depends on the type of work and can vary from 8 weeks to 6 months How long should I get the injections for DVT? 30 days When can I shower? As soon as the wound is dry, a waterproof bandage can be applied so that showering is possible!
How long will I stay in hospital? Classic 1 night.
Complications? Blood clotting and phlebitis may occur. If these clots break free, they can travel to the lungs and cause a life-threatening pulmonary embolism. To minimize this risk, injections with a blood thinner are therefore given for 30 days. Infections are rarely seen but can occur either around the wound or deeper around the plate. Superficial wound infections can in most cases be treated with antibiotics. Deep infections usually require additional surgery. Antibiotics are given during the procedure to minimize the risk of infection. Delayed healing of the osteotomy is more common in smokers and diabetics. Smoking cessation is therefore recommended for this type of procedure!